
Phase 2: Editing the plot display using attributes from the chart line object ‘p’.Python Dictionaries Access Items Change Items Add Items Remove Items Loop Dictionaries Copy Dictionaries Nested Dictionaries Dictionary Methods Dictionary Exercise Python If.Else Python While Loops Python For Loops Python Functions Python Lambda Python Arrays Python Classes/Objects Python Inheritance Python Iterators Python Polymorphism Python Scope Python Modules Python Dates Python Math Python JSON Python RegEx Python PIP Python Try.
#Plot lines matlab line style code
The code below generates two linear curves and edits the display of the graphs by altering the attributes of the chart line object. For example, this code specifies three line styles. To specify additional line styles, set the LineStyleOrder property of the axes. By default, there is only one line style (a solid line). The generated plot gets assigned to a chart line object, and its display gets customized by altering the attributes from the storing chart line object. MATLAB also cycles through different line styles in addition to colors. Matlab extends its feature in 2D line plots to customize the plot presentation through the execution even after the plot is generated. Downloading it, then using the following code (in the same directory where patchline was saved) x 1:10 y1 rand (size (x)) y2 rand (size (x)) 圓 rand (size (x)) figure hold all p1 patchline (x,y1,'edgecolor', 0.4 0.4 0.4.
#Plot lines matlab line style Patch
Plot(x,y1,x,y2,'-o','MarkerIndices',1:1:50)Ĭustomizing the presentation of the lines after the creation of the plot. There is this function called patchline (), which essentially draws your plots as patch objects instead. The below example generates 2 line plots, and we highlight one plot with the marker symbol ‘-o’. In the case of a graph containing lines more than three and having overlapped presentation, it helps to determine which data point belongs to which plot. Markers help point out distinct data points on the plotted line to determine the exact values calculated from the function. The code snippet below generates six lines for the function defined by ‘y’, the looping variable’ x’ function.ĭisplaying markers for specific data points for the lines.

If I specify a set of linestyles, plot cycles through all the colors on the first style, then all the colors on the second style, and so on. Use the hold on command to plot the two lines separately. I want to plot lines that differ in both linestyle and linecolor (because if someone makes a b&w copy of the paper, they lose the linecolor information). Return the two Line objects as an output argument from the plot function and then set the LineWidth property for each. This can also be achieved by calling the plot function in a loop where the plotting function can be defined as a function of the looping variable. To plot two lines with different line widths, you can use either of these approaches. Matlab enables users to plot more than two lines in a single plane. The code displays the data mapping each line to its corresponding plotting function. Including legend to distinguish the line plots: Application of the attribute ‘legend’ adds information to the plot to guide the user in identifying the lines with respect to their plotting functions. %Placing the second line plot in the second cell of the frame %Placing the first line plot in the first cell of the frame The below example presents 2 line plots generated from one single execution of the program with two different sets of axes. Arranging multiple line plots in different subplots: Matlab supports presenting the line plots generated in a single execution with a distinct set of axes. %The minimum value of the y-axis gets updated to -0.1 and the maximum value for the x-axis is updated to 12. Syntax to incorporate axes limit: axis ( )Ĭode: plot(x, y1,x,y2), axis()
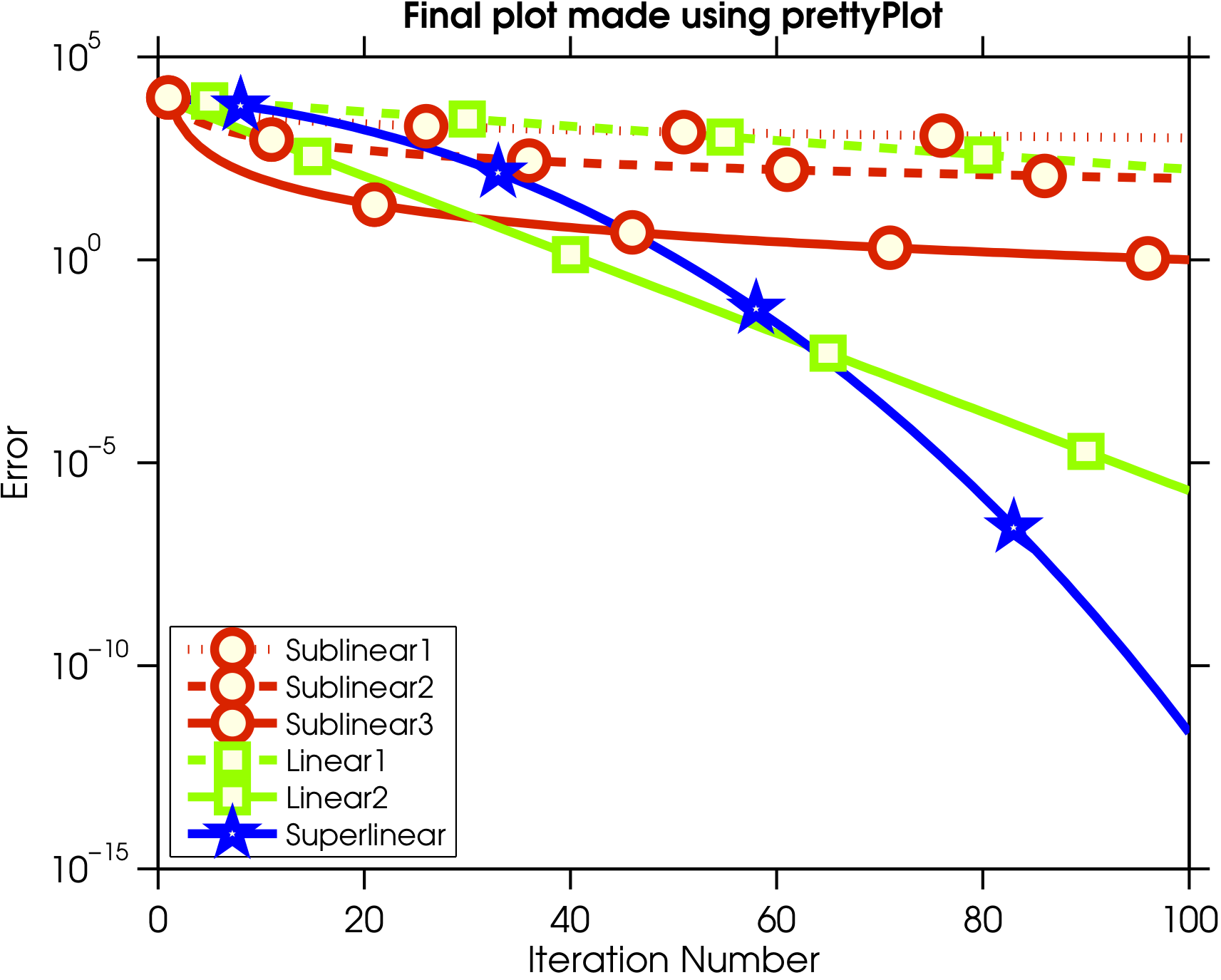
The limit values for the plots can be imposed on the axes using the command ‘axis’. Plot(x, y1,x,y2), xlabel('x-axis'), ylabel('y-axis'), title('Graph customisation'), %Adding x-label, y-label and title to the resultant plot The example defined below demonstrates the process of customization of the presentation of the graph by modifying the attributes given above. Axis square: A set of square plots can be generated. hline findobj (gcf, 'type', 'line') set (hline (1),'LineStyle',':') But that didnt seem to work.I added my graph. I have no basic data (anymore), but only the saved figure.

Axis equal: The plots can be created with a common scale factor and spaces for both axis.į. I would like to change the linestyle of a plotted graph for making color blind people to understand my graph. Grid on: Makes the grid lines visible for the graph.Į.
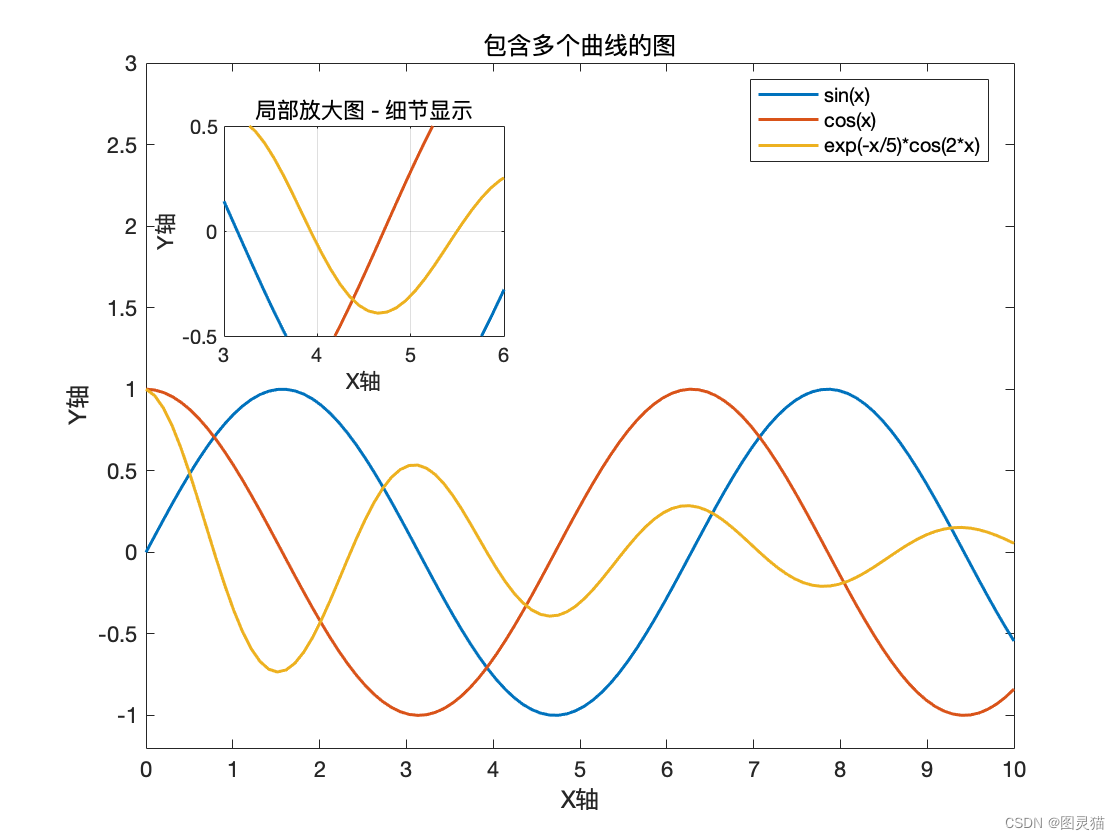
The customization of the lines drawn from single plot functions can be achieved by altering any of the attributes or any combination of the attributes described below:Ĭ. The resultant plot consists of 2 sinusoidal line curves, ‘y1’ and ‘y2′, having two different sets of values’,x1′ and ‘x2’, but share a common x-y plane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
